 Are you ready to understand how structures resist forces, deformations, and failures? In engineering, solid mechanics and structural analysis are the backbone of safe, efficient, and innovative designs. Without them, bridges could collapse, airplanes could fail, and machines would not work reliably. Today, we will explore this essential area step by step, like a classroom lecture.
Are you ready to understand how structures resist forces, deformations, and failures? In engineering, solid mechanics and structural analysis are the backbone of safe, efficient, and innovative designs. Without them, bridges could collapse, airplanes could fail, and machines would not work reliably. Today, we will explore this essential area step by step, like a classroom lecture.
What is Solid Mechanics?
Solid mechanics is the study of how solid materials respond to external forces, temperature variations, and other effects. In simple terms, it answers questions such as: Will this component deform too much? Will it resist the applied load?
This field forms the foundation of structural analysis. While solid mechanics explains the material behavior, structural analysis applies this knowledge to design entire systems—beams, frames, bridges, engines, and more.
Stress and Strain: The Language of Materials
To understand solid mechanics, we must begin with two essential concepts: stress and strain.
- Stress is the internal force per unit area inside a material.
- Strain is the measure of deformation, or how much the material stretches or compresses.
These two quantities are linked by material properties. For example, Hooke’s Law describes how, within the elastic range, stress is proportional to strain.
Mechanical Properties of Materials
Different materials behave in different ways. Some are strong but brittle, like glass. Others are ductile, like steel, which bends before breaking.
- Elastic modulus (Young’s modulus) – stiffness of the material.
- Yield strength – stress at which permanent deformation begins.
- Ultimate strength – maximum stress the material can withstand.
- Toughness – ability to absorb energy before failure.
Structural Analysis: Applying Solid Mechanics
While solid mechanics gives us the fundamentals, structural analysis applies them to real systems. Here we study how beams, trusses, columns, and complex frames react under forces.
 Types of Loads in Structures
Types of Loads in Structures
- Static loads: constant, such as the weight of a building.
- Dynamic loads: varying over time, such as vehicles crossing a bridge.
- Thermal loads: due to temperature expansion or contraction.
- Impact loads: sudden forces, like a hammer strike.
Failure Criteria and Safety
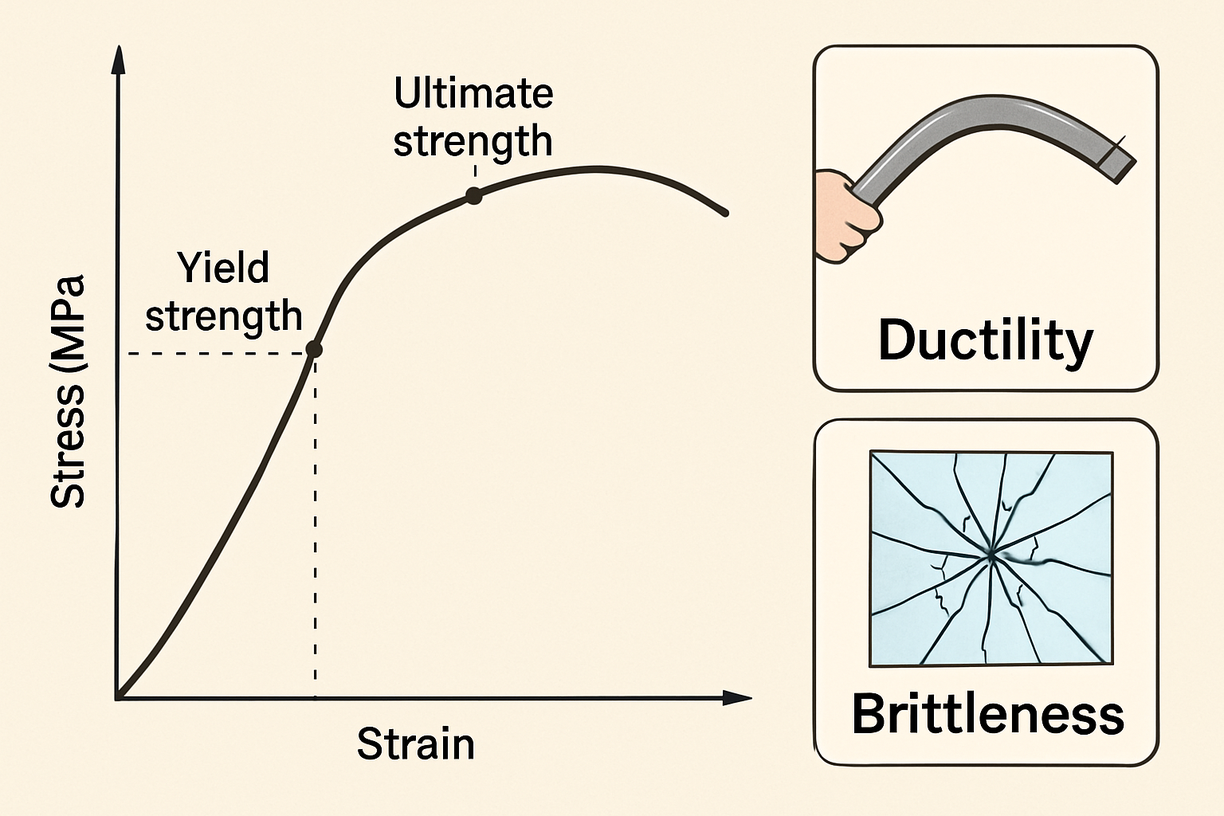
No analysis is complete without checking safety. Engineers use failure criteria to ensure designs are safe and functional.
- Maximum stress theory
- Von Mises criterion
- Mohr-Coulomb criterion
Buckling: A Critical Phenomenon
Columns under compression may fail suddenly through buckling—a lateral deflection that can occur even if the stress is below material strength.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA): A Modern Tool
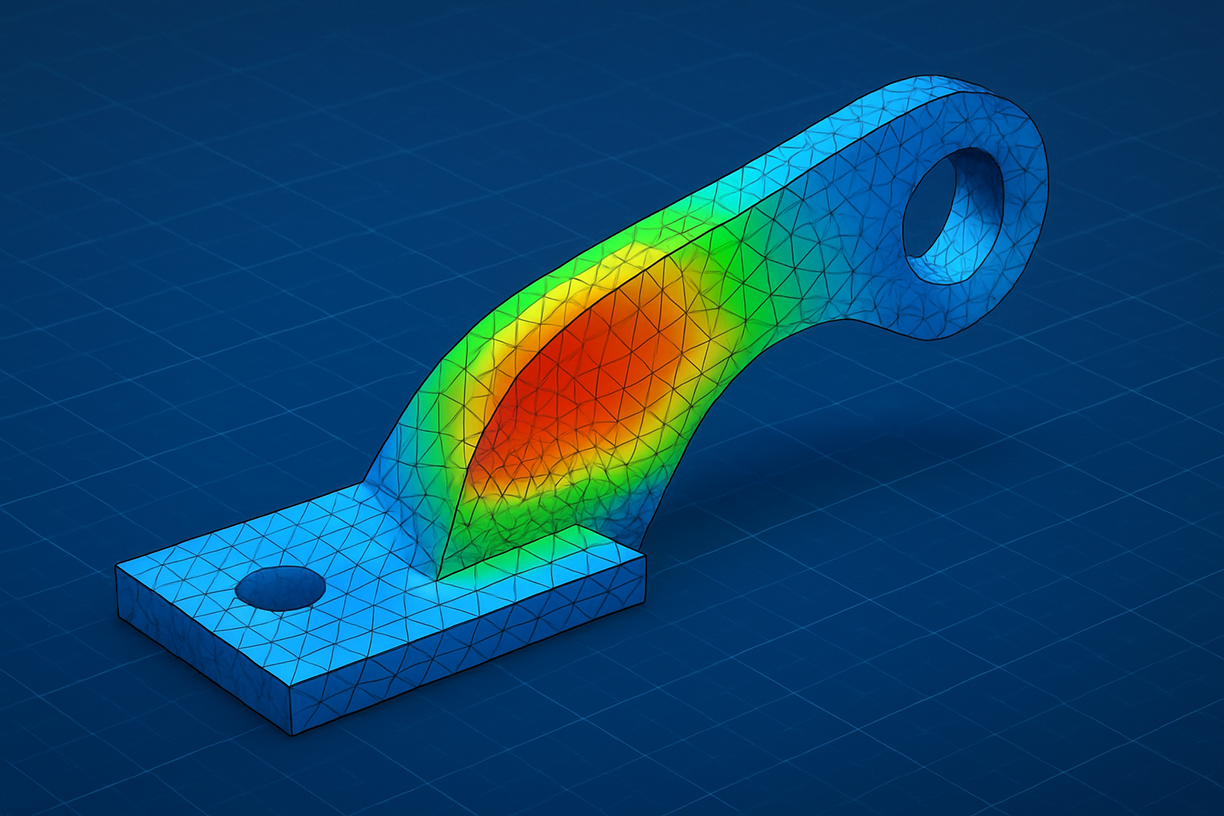
Today, engineers rarely calculate everything by hand. Instead, they use Finite Element Analysis (FEA), a powerful computational method that divides structures into elements to simulate stresses and deformations.
Integrated Workflow in Engineering
Solid mechanics, structural analysis, and tools like CAD/CAE/FEA now work together in an integrated process. This ensures faster design cycles, fewer errors, optimized resources, and safer products.
Practical Applications
- Civil engineering: skyscrapers, bridges, tunnels.
- Mechanical engineering: engines, machines, vehicles.
- Aerospace: aircraft structures, spacecraft.
- Energy sector: wind turbines, pipelines.
The Future of Solid Mechanics
Emerging technologies such as AI, digital twins, and real-time monitoring are revolutionizing how engineers design and maintain structures. Students of the future may test failures virtually before they happen in reality.
Conclusion
Solid mechanics and structural analysis are the foundation of engineering safety and innovation. By mastering these concepts, engineers ensure that every bridge, machine, and aircraft is both functional and reliable.
FAQ – Solid Mechanics and Structural Analysis
What is the difference between solid mechanics and structural analysis?
Solid mechanics studies how materials behave under loads, focusing on stress, strain, and material properties. Structural analysis applies this knowledge to entire systems like beams, bridges, or frames to ensure they can safely carry applied loads.
Why is solid mechanics important for engineers?
Solid mechanics is essential because it ensures the safety, reliability, and efficiency of machines, buildings, and structures. Without it, engineers could not predict how materials deform or fail under real-world conditions.
What are the main types of loads considered in structural analysis?
Engineers typically analyze static loads, dynamic loads, thermal loads, and impact loads. Each type affects structures differently and must be carefully studied during design.
What role does Finite Element Analysis (FEA) play in structural analysis?
FEA is a computational method that divides complex structures into smaller elements to calculate stresses, strains, and deformations. It allows engineers to simulate performance and reduce the need for costly prototypes.
Which industries use solid mechanics and structural analysis the most?
These fields are widely applied in civil engineering, aerospace, automotive, mechanical design, and energy sectors, ensuring safe and efficient designs in critical projects.



