Introduction: The Importance of Control Systems
When we talk about control systems, we are referring to the very heart of control and automation engineering. After all, they are responsible for keeping processes stable, predictable, and efficient. Imagine an airplane flying in turbulent conditions: without a robust control system, the pilot would not be able to keep the aircraft stable. Likewise, in an automated production line, it is the control system that ensures the final quality of the product.
Therefore, understanding control systems is essential for engineers and professionals who want to work in the development of modern technologies. In this post, we will explore the key concepts, present practical examples, and highlight the trends that shape the future of this field.
What Are Control Systems?
Simply put, control systems are structures that receive inputs, process information, and provide controlled outputs. In doing so, they keep physical variables such as temperature, pressure, or speed within desired values.
Open-loop and Closed-loop Systems
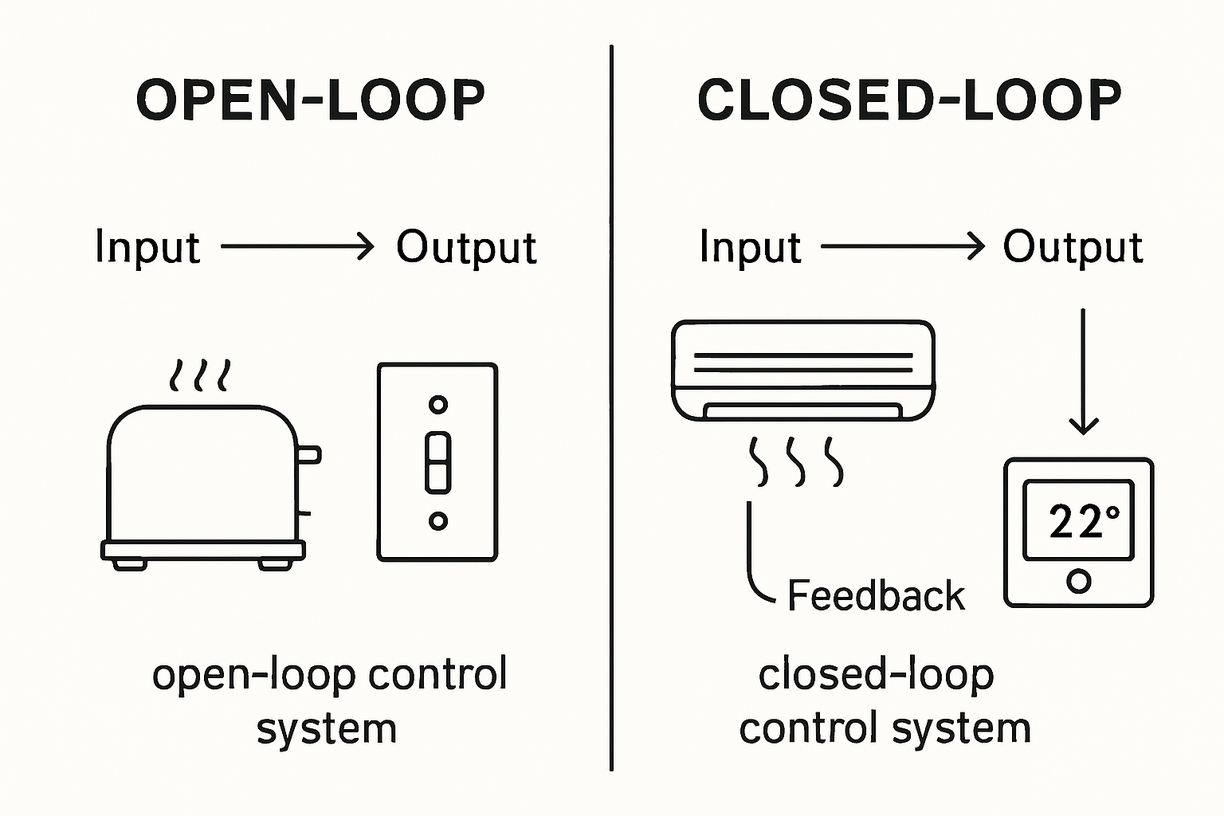
To better understand, let’s look at two basic classifications:
-
Open-loop system: does not use feedback. An electric oven, for example, heats up when turned on but does not measure the temperature to adjust it.
-
Closed-loop system: uses feedback. An air conditioner, for example, measures the room temperature and adjusts the compressor to maintain the value set by the user.
Note that while open-loop systems are simpler, closed-loop systems offer greater accuracy and stability.
The Importance of Control Systems in Modern Engineering
Looking at today’s world, we can see that practically every sector depends on these systems. Control systems are applied in:
-
Automotive industry: cruise control and vehicle stability.
-
Chemical industry: controlling temperature and pressure in reactors.
-
Electrical engineering: voltage regulation in generators.
-
Aeronautics: computer-assisted flight control.
Furthermore, industrial automation only became possible because control systems allowed the integration of sensors, actuators, and decision-making algorithms in real time.
Basic Structure of a Control System
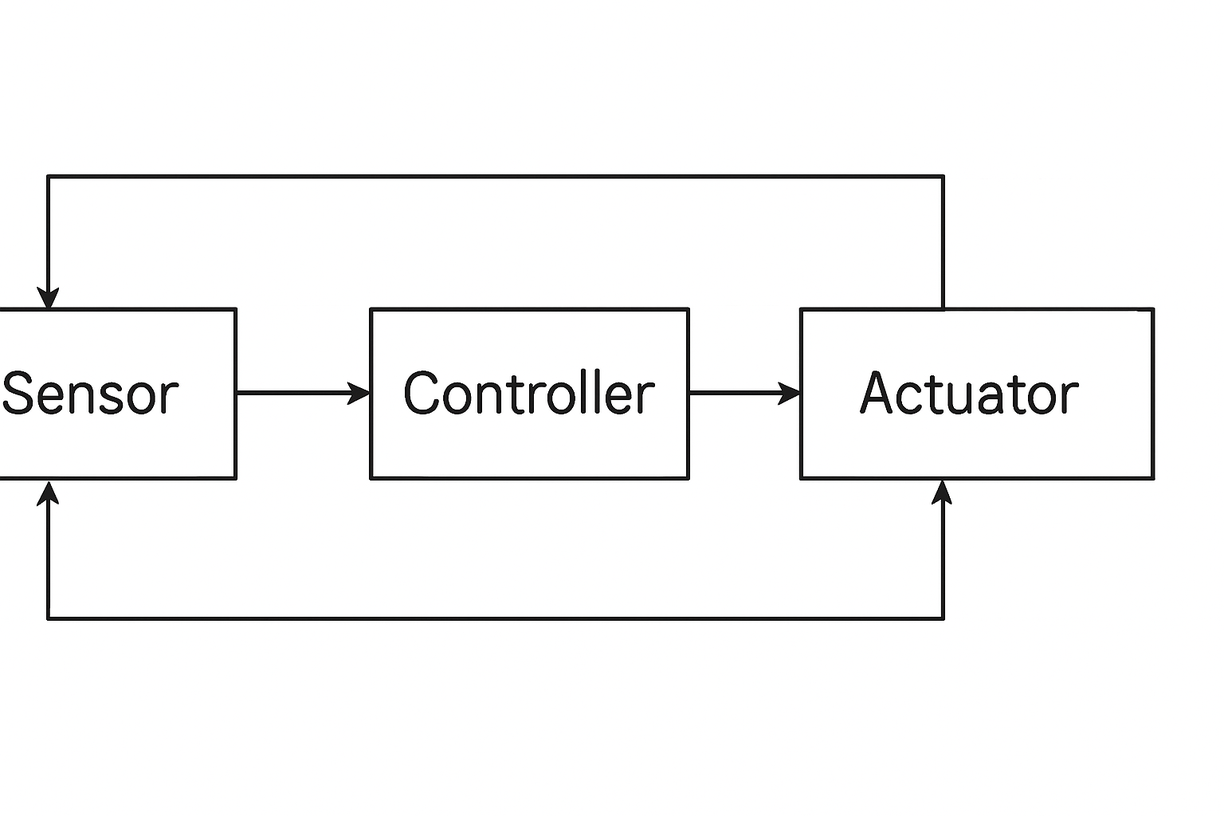
A control system can be represented by interconnected blocks. These blocks form a flow of information and actions:
-
Sensor: measures the variable of interest.
-
Controller: compares the measurement with the reference value.
-
Actuator: performs the action required to correct the variable.
-
Process: the physical system that undergoes the control action.
This way, we can see how each part contributes to keeping the system in balance.
Classical and Modern Control Techniques
PID Control
The proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controller is still one of the most widely used today. Its popularity comes from its simplicity and effectiveness in many applications.
Adaptive and Predictive Control
However, in more complex processes, modern methods have emerged, such as model predictive control (MPC). This type of system anticipates future behavior and adjusts the process even before significant deviations occur.
Artificial Intelligence Applications
In addition, artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly present. For example, intelligent control systems are now capable of learning from historical data to optimize industrial processes.
Future Trends in Control Systems
As Industry 4.0 continues to develop, control systems are becoming more connected, integrating IoT sensors, real-time communication networks, and big data algorithms.
Another key point is sustainability: new research seeks more energy-efficient control systems, reducing losses and contributing to environmental preservation.
Conclusion: The Engineer’s Role in Control Systems
Therefore, studying control systems is not just about mastering mathematical equations or block diagrams. More importantly, it is about understanding how to keep processes stable, safe, and efficient in a world that demands precision and reliability.
As teachers and professionals, we must remember that every controlled system has a direct impact on people’s lives. Whether in a simple household appliance or a space rocket, the principles remain the same.
Useful Links for Further Study
Also Read on Our Blog
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Control Systems
What are control systems?
They are structures that receive inputs, process information, and produce controlled outputs. In this way, they keep physical variables such as temperature and pressure within defined values.
What is the difference between open-loop and closed-loop systems?
In open-loop systems there is no feedback, as in a simple electric oven. In closed-loop systems, there is constant feedback, as in an air conditioner that measures the temperature and automatically adjusts its operation.
Where are control systems applied?
They are found in automobiles, aircraft, chemical plants, power plants, and even household appliances.
What is a PID controller?
It is a classical controller that combines three actions: proportional, integral, and derivative. It is widely used because it provides both simplicity and accuracy in dynamic systems.
How have control systems evolved in recent years?
Today, in addition to PID control, we have advanced methods such as predictive control and AI-based solutions, which make processes more intelligent and efficient.


